November is National Diabetes Awareness Month, one of the most complex chronic conditions to manage, as it involves several factors and can lead to many health complications.
Although the condition alters the endocrine function of the pancreas, when not managed well, it can affect almost every part of your body, including eyes, nervous system, blood circulation, kidneys, and even the ability for wounds to heal.
That is why it is so important to keep it under control so that you can have a good quality of life and avoid possible complications.
Here are the top 10 recommendations for optimal diabetes management:
#1—Know your condition well
The more you know about diabetes, the better you can take care of yourself and make the necessary changes to facilitate adherence to treatment and metabolic control.
#2—Eat a balanced diet
In general, you should consume food throughout the day, avoiding meals with a high amount of carbohydrates or meals that are quickly absorbed, as they raise glucose considerably. But, as several factors have to be considered, each person with diabetes should have a unique and personalized diet designed by her/his doctor and a nutritionist.
#3—Stay hydrated
People with diabetes have an increased risk of dehydration because an elevated blood glucose level causes the kidneys to try to eliminate it in the form of urine. That is why they tend to be thirstier when hyperglycemia occurs. Water should be the basis of hydration for a person with diabetes.
#4—Get regular physical activity
The practice of physical exercise is one of the fundamental pillars of the treatment of diabetes and prevents the associated complications. Its benefits occur at other levels, such as: it improves blood pressure, cholesterol and cardiovascular function. The type of exercise and intensity should be adapted to the age and physical condition of each person.
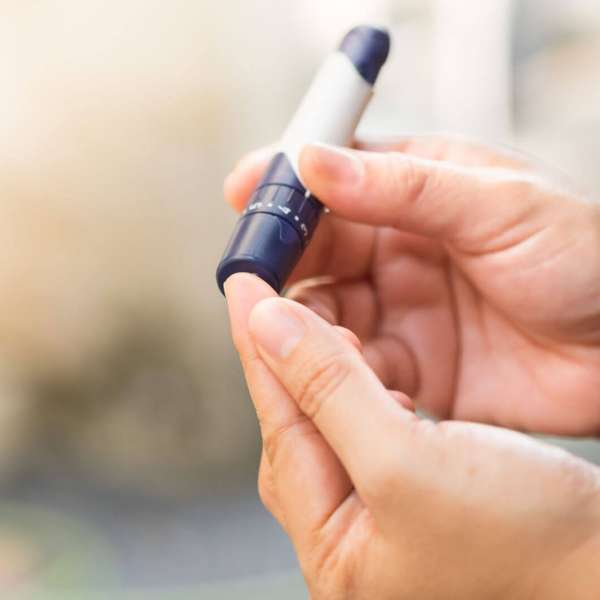
#5—Monitor your glucose
It is important to keep blood glucose levels at the optimal level before and after meals. For this, it is vital to analyze blood glucose levels several times a day since it allows you to know the level of glycemia at the moment and detect if glucose drops or rises. Your doctor will guide you on the monitoring routine you should follow.
#6—Get the A1C test quarterly
The A1C test is a blood test that provides information about average blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar, over the past three months. It is the main test used for diabetes management, monitoring the disease, and helping to make treatment decisions to avoid complications.
#7—Control your cholesterol and blood pressure
To avoid complications, you need to keep your blood pressure below 140/90. In addition, total cholesterol levels should be less than 200 mg/dl. A sedentary lifestyle and being overweight are factors that favor the appearance of LDL cholesterol or “bad cholesterol”, which means that low-density lipoproteins accumulate in the blood forming a plaque that is deposited in the arteries.
#8—Take care of your feet
People with diabetes may have impaired sensation and circulation. Therefore, it is important to perform a daily inspection of the feet to check for the absence of injuries, in addition to regularly visiting the podiatrist.
#9—Check your eyes
It is essential that people with diabetes perform periodic check-ups of their eyes, especially the state of the retina to prevent, detect and successfully treat any type of complication.
#10—Comply with your medication treatment
If you use insulin or any oral medication to control diabetes, you should do it just as the doctor prescribed. Don’t leave the doctor without clarifying the schedules and doses you should take and how food affects your medicines. Using medicines incorrectly puts you at greater risk of losing your vision, damaging your kidneys and nerves, and amputations. Be sure and learn about your health plan’s coverages and copays for treatment. Remember, you should always consult with your doctor about this and other health conditions to manage them correctly and live a healthy life.